shapes of distributions box plot When reviewing a box plot, an outlier is defined as a data point that is located outside the whiskers of the box plot. See more QILIPSU Waterproof Junction Box, IP67 Outdoor ABS Plastic Electrical Enclosure with Mounting Plate, Wall Brackets, Weatherproof Hinged Grey Cover for Projects (11.2"x7.7"x5.1")
0 · symmetric box and whisker plot
1 · skewness on a box plot
2 · skewed box and whisker plot
3 · shape of distribution skewed right
4 · shape of distribution skewed left
5 · right skewed data box plot
6 · right skewed box plot vertical
7 · explain box plot with example
Outdoor Electrical Box, Waterproof Electrical Junction Box IP65 ABS Plastic Enclosure with Fan & Thermostat, Mounting Plate and Hinged Lid (15.7" H x 11" L x 5.9" W)
Compare the respective medians of each box plot. If the median line of a box plot lies outside of the box of a comparison box plot, then there is likely to be a difference between the two groups. Source: https://blog.bioturing.com/2018/05/22/how-to-compare-box-plots/ See more
Compare the interquartile ranges (that is, the box lengths) to examine how the data is dispersed between each sample. The longer the box, the . See moreWhen reviewing a box plot, an outlier is defined as a data point that is located outside the whiskers of the box plot. See moreA box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of .
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.When a data set is graphed, each point is arranged to produce one of dozens of different shapes. The distribution shape can give you a visual which helps to show how the data is: Spread out (e.g. dispersion, variability, scatter), Where the .
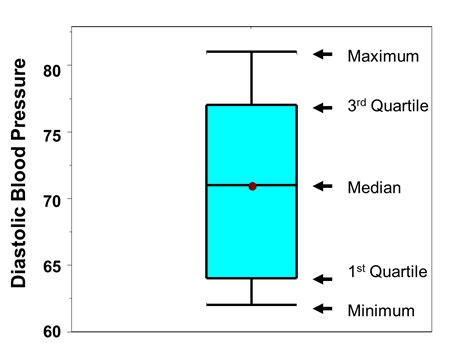
The shape of a distribution is described by its number of peaks and by its possession of symmetry, its tendency to skew, or its uniformity. (Distributions that are skewed have more points plotted on one side of the graph than on the . A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], .
Some distributions are symmetrical, with data evenly distributed about the mean. Other distributions are "skewed," with data tending to the left or right of the mean. We sometimes say .
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with .Symmetric (bell shaped) - when graphed, a vertical line drawn at the center will form mirror images, with the left half of the graph being the mirror image of the right half of the graph. In the histogram and dot plot, this shape is referred to as being a "bell shape" or a "mound".The most typical symmetric histogram or dot plot has the highest vertical column in the center.Explore your Data by using graphs and shapes of distributions. Graphs and shapes of Distributions. Learn about graphs and shapes of distributions with our comprehensive guide. From histograms to box plots, understand how to .The histogram and the box plot both group data together. Since histograms and box plots do not display each data value individually, they do not provide information about the shape of the distribution to the same level of detail that a dot plot does. This distribution, in particular, can also be called bell-shaped.
Symmetric (bell shaped) - when graphed, a vertical line drawn at the center will form mirror images, with the left half of the graph being the mirror image of the right half of the graph. In the histogram and dot plot, this shape is referred to as being a "bell shape" or a "mound".The most typical symmetric histogram or dot plot has the highest vertical column in the center.
symmetric box and whisker plot
Lesson 1: Distributions and Their Shapes Student Outcomes Students use informal language to describe the shape, center, and variability of a distribution based on a dot plot, histogram, or box plot. Students recognize that a first step in interpreting data is making sense of the context.
The box plots show the distribution of times spent shopping by two different groups. Questions : 1. . Compare the shapes of the box plots. The positions and lengths of the boxes and whiskers appear to be very similar. In both plots, the right whisker is shorter than the left whisker. 2.Find step-by-step Precalculus solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: These box plots show the basketball scores for two teams: Bulldogs: $\text{Min}=55,Q_1=70,Q_2=80,Q_3=90,\text{Max}=105$ Wolverines: $\text{Min}=35,Q_1=55,Q_2=80,Q_3=85,\text{Max}=96$ Compare the shapes of the box plots. .The mathematical purpose of this lesson is to describe distributions using the appropriate terminology. In order to learn more about different kinds of distributions, one thing students do is invent reasonable contexts for a given distribution. The terminology that is used is described here. In a symmetric distribution, the mean is equal to the median and there is a vertical line of .
mean is right in the center of the distribution. 3.If you have a display of the distribution such as a violin plot or a density plot, there’s another way to ˙nd the interval from one standard deviation below the mean to one standard deviation above the mean. First, ˙nd the peak of the display of the distribution. Then come down half way .
Box Plot is a graphical method to visualize data distribution for gaining insights and making informed decisions. Box plot is a type of chart that depicts a group of numerical data through their quartiles. . Information that are missed in a box plot is the detailed shape of the distribution. It is quite difficult to find the mean as it is .box-and-whisker plots, histograms, identify the shape of a distribution based on its interquartile ranges. Prerequisites. Students should already be familiar with. dot plots, box plots, and histograms, mean, median, mode, interquartile range. Join Nagwa Classes.About; Statistics; Number Theory; Java; Data Structures; Cornerstones; Calculus; Shape, Center, and Spread of a Distribution. A population parameter is a characteristic or measure obtained by using all of the data values in a population.. A sample statistic is a characteristic or measure obtained by using data values from a sample.. The parameters and statistics with which we . Box Plots. We have already discussed techniques for visually representing data (see histograms and frequency polygons). In this section we present another important graph, called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
These box plots show the basketball scores for two teams. Compare the shapes of the box plots Get the answers you need, now! . Write a five-number summary for each distribution: Bulldogs: Min: 55. Q1: 70. Med: 80. Q2: 90. Max: 105. Find step-by-step Algebra 2 solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Describe the shape of the data distributions. Explain how the dot plot and the box plot are smiliar and different.. . Box plots display data distribution according to a five-number summary, minimum value, first quartile, median, third quartile, and .In a symmetric distribution, the mean is equal to the median and there is a vertical line of symmetry in the center of the data display.The histogram and the box plot both group data together. Since histograms and box plots do not display each data value individually, they do not provide information about the shape of the distribution to the same level of detail that a dot plot .
These simple plots also can produce ambiguities. A boxplot, for instance, can obscure the nature of an underlying distribution, reducing unimodal, bimodal, and skewed distributions to similar or .Symmetric (bell shaped) - when graphed, a vertical line drawn at the center will form mirror images, with the left half of the graph being the mirror image of the right half of the graph. In the histogram and dot plot, this shape is referred to as being a "bell shape" or a "mound".The most typical symmetric histogram or dot plot has the highest vertical column in the center.and symmetry to describe the shape of the distribution. shape of the distribution. Example 2 6. SCHOOL The box-and-whisker plot shows the science test scores for Mrs. Everly’s students. Describe the shape of the distribution using symmetry and outliers. 7. DONATIONS The box-and-whisker plot shows the donations in dollars to charity by several . A box plot is a type of plot that displays the five number summary of a dataset, which includes: The minimum value; The first quartile (the 25th percentile) The median value; The third quartile (the 75th percentile) The maximum value; We use the following process to draw a box plot: Draw a box from the first quartile (Q1) to the third quartile (Q3)
A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, provides a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics and shows the spread and central tendency of the data. The box plot includes the following information. Minimum: The smallest value in the dataset, excluding any outliers.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Box and whisker plots, Contingency table, Cross-tabulation and more. . Graphic representations of central tendencies, percentiles, variabilities, and the shapes of frequency distributions. Contingency table. A data matrix that displays the frequency of some combination of . For a scalar random variable, the following plots are all useful depictions of the distribution: The box plot: This is a simple plot that shows various quantiles of the data using a standard box-and-whiskers method, as well as showing "outliers" that are outside some multiple of the interquartile range. This plot gives a simple sense of where the bulk of the data lies, via .Shapes of Box-and-Whisker Plots . Most data on the left A box-and-whisker plot also shows the shape of a distribution. Section 10.4 Box-and-Whisker Plots 463 9 +(- 6 )= 3 3 +(- 3 )= 4 +(- 9 )= 9 +(- 1 )= 4. The box-and-whisker plots represent the daily attendance at two beaches during July. Compare and contrast the attendances for the two .
a distribution that can be divided at the center so each half is the mirror of the other. Box Plot. A diagram of range, median, and interquartile range. Median. A measure of center found by determining the middle number in a data set arranged in numerical order. Lower Quartile (Q1)A box plot is one of the most useful graphic displays that is still used today. These simple plots communicate a great deal of information about the central tendency, variability, and shape of the distribution of responses. When placed side by side, box plots can be used effectively to compare results across variables, products, or groups.Box plots summarize data on an interval scale, showing distribution shape, central value, and variability 3. They display data from a five-number summary: minimum, Q1, median, Q3, and maximum. Box plots help identify skewed distributions and outliers 3. The box plot includes the minimum, Q1, median, Q3, and maximum.
skewness on a box plot
$9.99
shapes of distributions box plot|skewness on a box plot