calculating the charge inside a box with electric field 1. Charge and Electric Flux - A charge distribution produces an electric field (E), and E exerts a force on a test charge (q 0). By moving q 0 around a closed box that contains the charge . Order Floor Jacks, Plugs and Electrical Floor Boxes from WiremoldProducts.com. Easily choose the business phone equipment and phone system solution that is right for your company. Buy .
0 · net charge in physics
1 · how to calculate net charge
2 · how to calculate flux in electricity
3 · enclosed charge physics
but the easiest way to solve this is to pull new conductors from the panel of B to this box. The conduit is already there. But I have never seen or heard of two circuits from .
Determine the amount of charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface. This is an evaluation of the right-hand side of the equation representing Gauss’s law. It is often necessary to perform an integration to obtain the net enclosed charge. Evaluate the electric field of the charge distribution.Now, what happens to the electric flux if there are some charges inside the . Knowing that a charge distribution produces an electric field, we can measure on the surface of the box to determine what is inside the box. Recall that the electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and radially in .Now, what happens to the electric flux if there are some charges inside the enclosed volume? Gauss’s law gives a quantitative answer to this question. To get a feel for what to expect, let’s calculate the electric flux through a spherical .
1. Charge and Electric Flux - A charge distribution produces an electric field (E), and E exerts a force on a test charge (q 0). By moving q 0 around a closed box that contains the charge .
To calculate the charge inside a box using Gauss Law and Flux, first choose a closed surface that encloses the box. Then, calculate the flux through that surface and equate .Describe line charges, surface charges, and volume charges; Calculate the field of a continuous source charge distribution of either sign The example below shows how to determine the net charge located inside a box and is fundamental to understanding Gauss's Law. It demonstrates the idea that to calculate the net charge inside a box, we have .
Gauss’s law will allow us to do electric-field calculations using symmetry principles. • Positive charge within the box produces outward electric flux through the surface of the box, and .
Gauss’s Law is used to find the electric field when a charge distribution is given. We can apply Gauss’s Law using analytical expressions only to a specific set of symmetric charge distributions. The key to finding the Electric field from .It is possible to determine the net charge inside by box, by first calculating the electric field by a test charge and then calculating the electric flux by using Gauss’s law.Determine the amount of charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface. This is an evaluation of the right-hand side of the equation representing Gauss’s law. It is often necessary to perform an integration to obtain the net enclosed charge. Evaluate the electric field of the charge distribution. Knowing that a charge distribution produces an electric field, we can measure on the surface of the box to determine what is inside the box. Recall that the electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and radially in toward a negative point charge.
Now, what happens to the electric flux if there are some charges inside the enclosed volume? Gauss’s law gives a quantitative answer to this question. To get a feel for what to expect, let’s calculate the electric flux through a spherical surface around a positive point charge \(q\), since we already know the electric field in such a situation.1. Charge and Electric Flux - A charge distribution produces an electric field (E), and E exerts a force on a test charge (q 0). By moving q 0 around a closed box that contains the charge distribution and measuring F one can make a 3D map of E = F/q 0 outside the box. From that map, we can obtain the value of q inside box. To calculate the charge inside a box using Gauss Law and Flux, first choose a closed surface that encloses the box. Then, calculate the flux through that surface and equate it to the total charge enclosed by the surface. This will give you the value of the charge inside the box.Describe line charges, surface charges, and volume charges; Calculate the field of a continuous source charge distribution of either sign
The example below shows how to determine the net charge located inside a box and is fundamental to understanding Gauss's Law. It demonstrates the idea that to calculate the net charge inside a box, we have to start off by calculating the fluxes acting on all surfaces on the box by using the Gauss's Law.
net charge in physics
how to calculate net charge
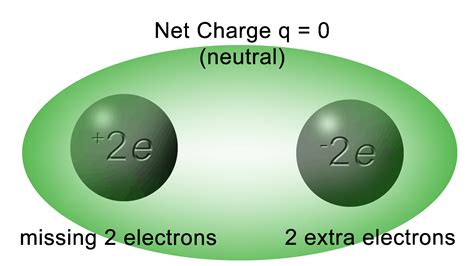

Gauss’s law will allow us to do electric-field calculations using symmetry principles. • Positive charge within the box produces outward electric flux through the surface of the box, and negative charge produces inward flux. (See Figure 22.2 below.)
Gauss’s Law is used to find the electric field when a charge distribution is given. We can apply Gauss’s Law using analytical expressions only to a specific set of symmetric charge distributions. The key to finding the Electric field from Gauss’s Law is selecting the simplest surface to perform the integration in Equation eq:gaussLaw.
It is possible to determine the net charge inside by box, by first calculating the electric field by a test charge and then calculating the electric flux by using Gauss’s law.
Determine the amount of charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface. This is an evaluation of the right-hand side of the equation representing Gauss’s law. It is often necessary to perform an integration to obtain the net enclosed charge. Evaluate the electric field of the charge distribution.
Knowing that a charge distribution produces an electric field, we can measure on the surface of the box to determine what is inside the box. Recall that the electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and radially in toward a negative point charge.Now, what happens to the electric flux if there are some charges inside the enclosed volume? Gauss’s law gives a quantitative answer to this question. To get a feel for what to expect, let’s calculate the electric flux through a spherical surface around a positive point charge \(q\), since we already know the electric field in such a situation.1. Charge and Electric Flux - A charge distribution produces an electric field (E), and E exerts a force on a test charge (q 0). By moving q 0 around a closed box that contains the charge distribution and measuring F one can make a 3D map of E = F/q 0 outside the box. From that map, we can obtain the value of q inside box. To calculate the charge inside a box using Gauss Law and Flux, first choose a closed surface that encloses the box. Then, calculate the flux through that surface and equate it to the total charge enclosed by the surface. This will give you the value of the charge inside the box.
Describe line charges, surface charges, and volume charges; Calculate the field of a continuous source charge distribution of either sign The example below shows how to determine the net charge located inside a box and is fundamental to understanding Gauss's Law. It demonstrates the idea that to calculate the net charge inside a box, we have to start off by calculating the fluxes acting on all surfaces on the box by using the Gauss's Law.
Gauss’s law will allow us to do electric-field calculations using symmetry principles. • Positive charge within the box produces outward electric flux through the surface of the box, and negative charge produces inward flux. (See Figure 22.2 below.)Gauss’s Law is used to find the electric field when a charge distribution is given. We can apply Gauss’s Law using analytical expressions only to a specific set of symmetric charge distributions. The key to finding the Electric field from Gauss’s Law is selecting the simplest surface to perform the integration in Equation eq:gaussLaw.

how to calculate flux in electricity
enclosed charge physics
I brought the cable into the box using a duplex clamp and am left with wiring that is too short. What is the best and safest way to extend this wiring without having to go into the attic replace it completely?
calculating the charge inside a box with electric field|how to calculate flux in electricity