determining shape of distribution box plot Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed . Embrace ShopSabre CNC Routers and seize ultimate control over your machining and woodworking endeavors, even in a small shop. From sign-making to cabinet shop production, aerospace, and more, our CNC machines have what it takes, making them the perfect choice for any project, and will be for years to come.
0 · symmetric box and whisker plot
1 · skewness on a box plot
2 · skewed box and whisker plot
3 · shape of distribution skewed right
4 · shape of distribution skewed left
5 · right skewed data box plot
6 · right skewed box plot vertical
7 · explain box plot with example
FANUC has the largest inventory of new and refurbished CNC replacement parts to make sure your operations run smooth. In-stock FANUC CNC parts ordered before 5:00 pm ship the same day and can typically be delivered from our central warehouse in less than 24 hours.
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum .
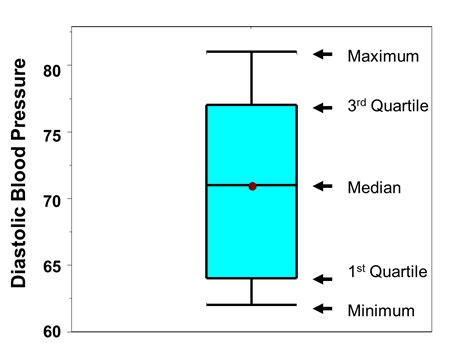
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or .
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
You can tell the shape of the histogram (distribution) - in many cases at least - by just looking the box plot, and you can also estimate whether the mean is less than or greater than the median.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with .Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles. From .
When the median is in the middle of the box and the whiskers are roughly equal on each side, the distribution is symmetrical (or “no” skew). The following examples illustrate how to use box plots to determine if a distribution is right-skewed, left-skewed, or has no skew. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right. In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or symmetrical, provides crucial insights into data characteristics.Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.You can tell the shape of the histogram (distribution) - in many cases at least - by just looking the box plot, and you can also estimate whether the mean is less than or greater than the median.
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.
jk metal fabrication & design
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.
Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles. From this, the spread and skew of the data can also be seen. When the median is in the middle of the box and the whiskers are roughly equal on each side, the distribution is symmetrical (or “no” skew). The following examples illustrate how to use box plots to determine if a distribution is right-skewed, left-skewed, or has no skew.
symmetric box and whisker plot
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.
In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or symmetrical, provides crucial insights into data characteristics.Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.You can tell the shape of the histogram (distribution) - in many cases at least - by just looking the box plot, and you can also estimate whether the mean is less than or greater than the median.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.
skewness on a box plot
skewed box and whisker plot
Check out our indian metal box selection for the very best in unique or custom, handmade pieces from our boxes & bins shops.
determining shape of distribution box plot|shape of distribution skewed left