electric field inside a box 1. Charge and Electric Flux - A charge distribution produces an electric field (E), and E exerts a force on a test charge (q 0). By moving q 0 around a closed box that contains the charge . The X-ACTO Small Mitre Box is the perfect guide to making precision cuts in all your modeling, craft and home improvement projects. The convenient mitre box features slotted sides for accurate mitres on even the smallest projects.
0 · homework and exercises
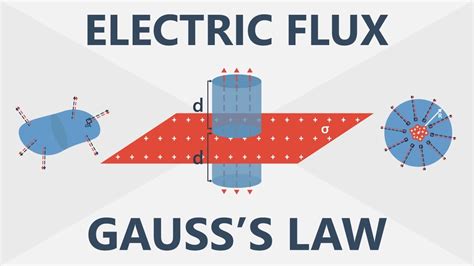
1 · The Basics of Electric Flux and Gauss’s Law
2 · The Basics of Electric Flux and Gauss’s Law
3 · Flux Through A Closed Box
4 · Electric field inside a uniformly charged cubical box
5 · Chapter 22 – Gauss Law
6 · Calculation of electric field using Gauss’s Law
7 · 6.4: Applying Gauss’s Law
8 · 6.3: Explaining Gauss’s Law
9 · 6.3 Applying Gauss’s Law
10 · 6.2: Electric Flux
The X-Carve Pro CNC Solution for Cabinet & Furniture Makers. Combining Hardware and Easy-to-Use Software - No Experience Needed for Professional Results.
Gauss’s law is very helpful in determining expressions for the electric field, even though the law is not directly about the electric field; it is about the electric flux. It turns out that in situations that have certain symmetries (spherical, cylindrical, . Knowing that a charge distribution produces an electric field, we can measure on the surface of the box to determine what is inside the box. Recall that the electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and radially in .According to Gauss’s law, the flux of the electric field →E through any closed surface, also called a Gaussian surface, is equal to the net charge enclosed (qenc) divided by the permittivity of free space (ϵ0):1. Charge and Electric Flux - A charge distribution produces an electric field (E), and E exerts a force on a test charge (q 0). By moving q 0 around a closed box that contains the charge .
Find the electric field (a) at a point outside the shell and (b) at a point inside the shell. Strategy Apply the Gauss’s law strategy given earlier, where we treat the cases inside and outside the shell separately. Solution. Electric field at a point . The electric field inside a uniformly charged cubical box refers to the strength and direction of the force experienced by a charged particle placed inside the box. It is determined .
This animation shows how the electric field at points on the surface of a box (and hence the flux through box's surface) depends upon the sign and location o.Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) shows the electric field of an oppositely charged, parallel-plate system and an imaginary box between the plates. The electric field between the plates is uniform and points from the positive plate toward the negative plate.

Gauss’s Law is used to find the electric field when a charge distribution is given. We can apply Gauss’s Law using analytical expressions only to a specific set of symmetric charge distributions. The key to finding the Electric field from . What is the electric field/potential inside the box as a function of time and space?Gauss’s law is very helpful in determining expressions for the electric field, even though the law is not directly about the electric field; it is about the electric flux. It turns out that in situations that have certain symmetries (spherical, cylindrical, or planar) in the charge distribution, we can deduce the electric field based on .
Knowing that a charge distribution produces an electric field, we can measure on the surface of the box to determine what is inside the box. Recall that the electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and radially in toward a negative point charge.According to Gauss’s law, the flux of the electric field →E through any closed surface, also called a Gaussian surface, is equal to the net charge enclosed (qenc) divided by the permittivity of free space (ϵ0):1. Charge and Electric Flux - A charge distribution produces an electric field (E), and E exerts a force on a test charge (q 0). By moving q 0 around a closed box that contains the charge distribution and measuring F one can make a 3D map of E = F/q 0 outside the box. From that map, we can obtain the value of q inside box.
Find the electric field (a) at a point outside the shell and (b) at a point inside the shell. Strategy Apply the Gauss’s law strategy given earlier, where we treat the cases inside and outside the shell separately. Solution. Electric field at a point outside the shell. The electric field inside a uniformly charged cubical box refers to the strength and direction of the force experienced by a charged particle placed inside the box. It is determined by the distribution of electric charges within the box.

This animation shows how the electric field at points on the surface of a box (and hence the flux through box's surface) depends upon the sign and location o.
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) shows the electric field of an oppositely charged, parallel-plate system and an imaginary box between the plates. The electric field between the plates is uniform and points from the positive plate toward the negative plate.Gauss’s Law is used to find the electric field when a charge distribution is given. We can apply Gauss’s Law using analytical expressions only to a specific set of symmetric charge distributions. The key to finding the Electric field from Gauss’s Law is selecting the simplest surface to perform the integration in Equation eq:gaussLaw. What is the electric field/potential inside the box as a function of time and space?
homework and exercises
Gauss’s law is very helpful in determining expressions for the electric field, even though the law is not directly about the electric field; it is about the electric flux. It turns out that in situations that have certain symmetries (spherical, cylindrical, or planar) in the charge distribution, we can deduce the electric field based on .
Knowing that a charge distribution produces an electric field, we can measure on the surface of the box to determine what is inside the box. Recall that the electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and radially in toward a negative point charge.According to Gauss’s law, the flux of the electric field →E through any closed surface, also called a Gaussian surface, is equal to the net charge enclosed (qenc) divided by the permittivity of free space (ϵ0):1. Charge and Electric Flux - A charge distribution produces an electric field (E), and E exerts a force on a test charge (q 0). By moving q 0 around a closed box that contains the charge distribution and measuring F one can make a 3D map of E = F/q 0 outside the box. From that map, we can obtain the value of q inside box.
Find the electric field (a) at a point outside the shell and (b) at a point inside the shell. Strategy Apply the Gauss’s law strategy given earlier, where we treat the cases inside and outside the shell separately. Solution. Electric field at a point outside the shell.
The electric field inside a uniformly charged cubical box refers to the strength and direction of the force experienced by a charged particle placed inside the box. It is determined by the distribution of electric charges within the box.This animation shows how the electric field at points on the surface of a box (and hence the flux through box's surface) depends upon the sign and location o.Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) shows the electric field of an oppositely charged, parallel-plate system and an imaginary box between the plates. The electric field between the plates is uniform and points from the positive plate toward the negative plate.Gauss’s Law is used to find the electric field when a charge distribution is given. We can apply Gauss’s Law using analytical expressions only to a specific set of symmetric charge distributions. The key to finding the Electric field from Gauss’s Law is selecting the simplest surface to perform the integration in Equation eq:gaussLaw.
The Basics of Electric Flux and Gauss’s Law
XACT HVAC Inc. is a family owned company offering decades of experience. It all started in 1995 when Carlos Oliveira, now Director of X-ACT Sheet Metal Inc., decided to get into the HVAC industry. Through hard work and dedication, he was able to become a master in his trade and founded X-ACT Sheet Metal Inc. in 2005.
electric field inside a box|6.3 Applying Gauss’s Law